The world is facing a serious threat from antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to human and animal health, food production, and environmental health. In response, the Quadripartite group of organisations – the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), and the World Health Organization (WHO) – jointly advocate for AMR awareness through various efforts and activities throughout the year.
These initiatives promote the prudent use of antimicrobial agents, fosters cross-sectoral collaboration, and collectively protect the effectiveness of antimicrobials for future generations.
To demonstrate its commitment to combating AMR, Chinese Taipei approved the “National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (2021-2025)” in 2021, jointly proposed by the government’s Ministry of Agriculture (MOA) and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW). The plan adopts the One Health approach to address AMR. This national action plan spans the human, animal, plant, and environmental sectors, leveraging inter-ministerial collaboration to implement AMR prevention policies and initiatives. The key actions include:
In 2024, Chinese Taipei joined the international call to action under the theme of “Education, Advocacy, and Immediate Action,” implementing measures for stakeholders to collaboratively prevent the crisis caused by AMR.
At the start of 2025, Chinese Taipei launched the “National One Health AMR Management Action 5-Year Plan” through cross-agency collaboration to mitigate the threat of AMR. The plan focuses on implementing five key strategies:
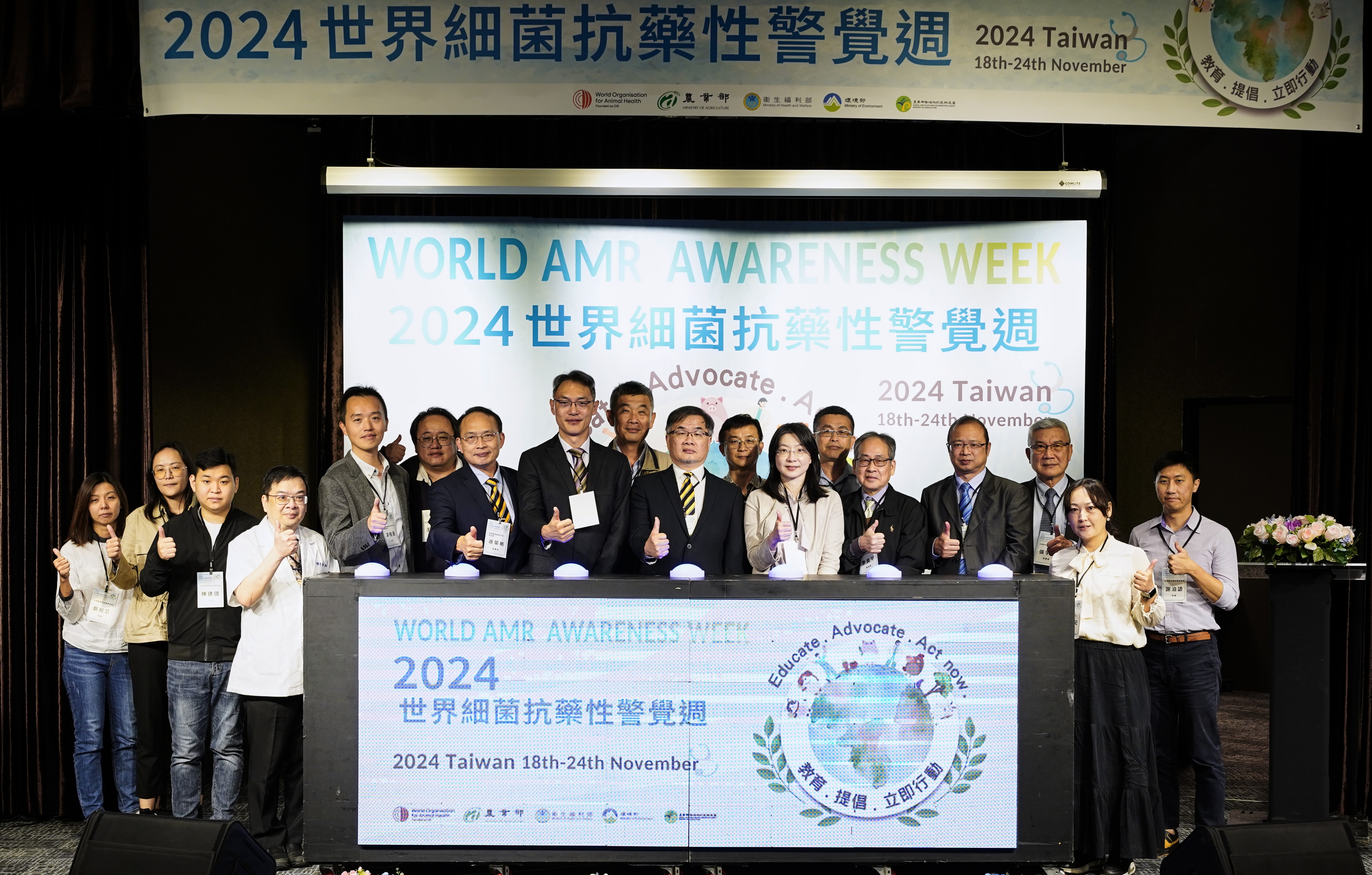
(Nov 2024) WAAW 2024 event to raise awareness on AMR.
Educate: Building Professional Capabilities of AMR
The MOA has implemented a series of training programs to enhance the understanding and response capabilities of professionals and stakeholders regarding AMR. Initiatives include awareness campaigns for veterinary students, training for veterinarians, and education sessions for pet-keeping businesses on the prudent use of antimicrobials.
Moreover, to provide guidelines on AMR for companion animal veterinary institutions, we extracted sections relevant to Chinese Taipei’s situations from the 2020 publication by Japan’s Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, “Guidelines for Prudent Use of Antimicrobials in Companion Animals.” After consolidating and revising these materials with input from domestic experts, we published the “Handbook on Prudent Use of Antimicrobials in Companion Animals.” This guideline aims to promote the prudent use of antimicrobials, mitigate AMR, and protect the effectiveness of antimicrobials, ensuring that effective antimicrobials remain available when companion animals require treatment.
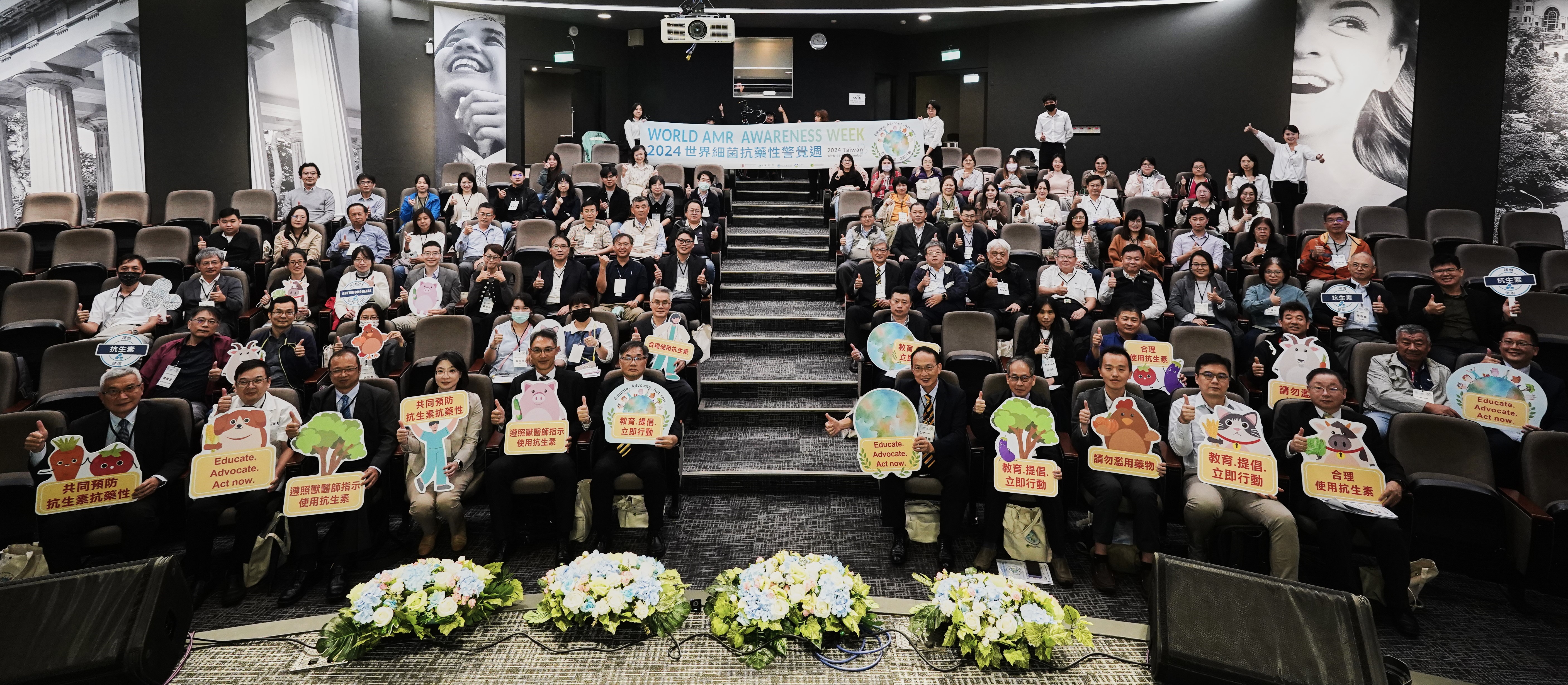
(Nov 2024) WAAW 2024 event to raise awareness on AMR.
Advocate: Raising Public Awareness of AMR
In response to the Quadripartite organizations’ awareness initiative to celebrate “World AMR Awareness Week (WAAW)” annually every November 18 to 24, Chinese Taipei has held annual activities to raise awareness and understanding of AMR during WAAW, beginning in 2020. These efforts are jointly supported by Chinese Taipei’s Ministry of Health and Welfare, Ministry of the Environment, Ministry of Agriculture, national animal and plant health authorities, veterinary associations, university experts in veterinary and plant protection, and representatives from animal and plant industry groups. Together, they committed to promoting awareness of the prudent use of antimicrobials and enhancing understanding of AMR to collectively prevent the threats posed by AMR.
under the theme of "Education, Advocacy, and Immediate Action," implementing measures for stakeholders to collaboratively prevent the crisis caused by AMR.
(Nov 2024) A slide from a presentation given during WAAW 2024 at an event in Chinese Taipei.
To raise public awareness of AMR issues, the MOA launched an AMR awareness website in 2024 and organized an AMR knowledge quiz with prizes through the official Facebook of the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Agency (APHIA). These initiatives encourage public participation via AMR-related quizzes, gradually increasing attention to AMR while disseminating scientific knowledge to curb its spread. Additionally, the results of the “National Action Plan on AMR” (launched in January 2025) have been consolidated into manuals and videos to communicate research findings on AMR to the public. This effort aims to enhance public understanding of AMR and gather the public’s feedback to shape future AMR management policies.
Act Now: Strengthening Global Collaboration and AMR Monitoring
Chinese Taipei actively participates in international AMR workshops, sharing its expertise and progress. In 2024, Chinese Taipei attended the ISAH & SEAOHUN International Conference 2024 to present its AMR management initiatives. In addition, the “International Symposium on Pest Resistance Management in Crops” held on 22-23 October 2024, invited experts from the United States, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and CropLife Asia to deliver presentations on herbicides, Miteicides, antibacterial agents, and insecticides. The symposium also facilitated discussions and exchanges on new technologies and management trends to gain insights into the latest advancements and applications in pest resistance management across different countries and regions. This collaborative effort aims to contribute to the realisation of One Health and sustainable agricultural development while promoting global knowledge sharing and technical exchanges.
Chinese Taipei has followed WOAH standards to establish an AMR monitoring system. AMR analysis of isolates is conducted using the latest standard methods issued by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). AMR monitoring is carried out for livestock, poultry, aquatic animals, and companion animals. At the same time, Chinese Taipei is developing intelligent modular environmental control systems, establishing high-biosecurity management models, and developing alternatives to antimicrobials to reduce their use as growth promoters. These efforts aim to enhance animal immunity and overall health, thereby reducing reliance on antimicrobials.
In the area of crops, Chinese Taipei also monitors AMR in plant pathogenic bacteria. Field-collected plant pathogenic bacteria are isolated and their susceptibility to plant-applied antimicrobials is tested.
Chinese Taipei as a global partner in combating AMR
As a global partner in combating AMR, Chinese Taipei is continuing to strengthen collaboration across various sectors, promote research and solutions for AMR issues, and work hand-in-hand with the international community to protect global health. Through the three pillars of “Education, Advocacy, and Immediate Action,” Chinese Taipei remains committed to fighting AMR.





